import time
import random
from typing import List, Dict, Tuple
def generate_test_array(size: int, zero_pairs_ratio: float = 0.3) -> List[int]:
"""Generate test array with controlled number of zero-sum pairs"""
arr = []
pairs_count = int(size * zero_pairs_ratio / 2)
# Add pairs that sum to zero
for i in range(pairs_count):
val = random.randint(1, 100)
arr.extend([val, -val])
# Add random numbers (unlikely to form pairs)
remaining = size - len(arr)
arr.extend(random.randint(101, 200) for _ in range(remaining))
random.shuffle(arr)
return arr
def benchmark_solutions(sizes: List[int] = [10, 50, 100, 500, 1000, 2000]) -> Tuple[List[int], Dict]:
"""Compare performance of all three approaches"""
results = {
'brute_force': {'times': [], 'operations': []},
'hash_table': {'times': [], 'operations': []},
'two_pointer': {'times': [], 'operations': []}
}
for size in sizes:
arr = generate_test_array(size)
# Benchmark brute force
start = time.perf_counter()
count, ops = two_sum_brute_force(arr)
results['brute_force']['times'].append(time.perf_counter() - start)
results['brute_force']['operations'].append(ops)
# Benchmark hash table
start = time.perf_counter()
count, ops = two_sum_hash_table(arr)
results['hash_table']['times'].append(time.perf_counter() - start)
results['hash_table']['operations'].append(ops)
# Benchmark two-pointer
start = time.perf_counter()
count, ops = two_sum_two_pointer(arr)
results['two_pointer']['times'].append(time.perf_counter() - start)
results['two_pointer']['operations'].append(ops)
return sizes, results
# Run benchmarks
sizes, results = benchmark_solutions()
# Visualize results
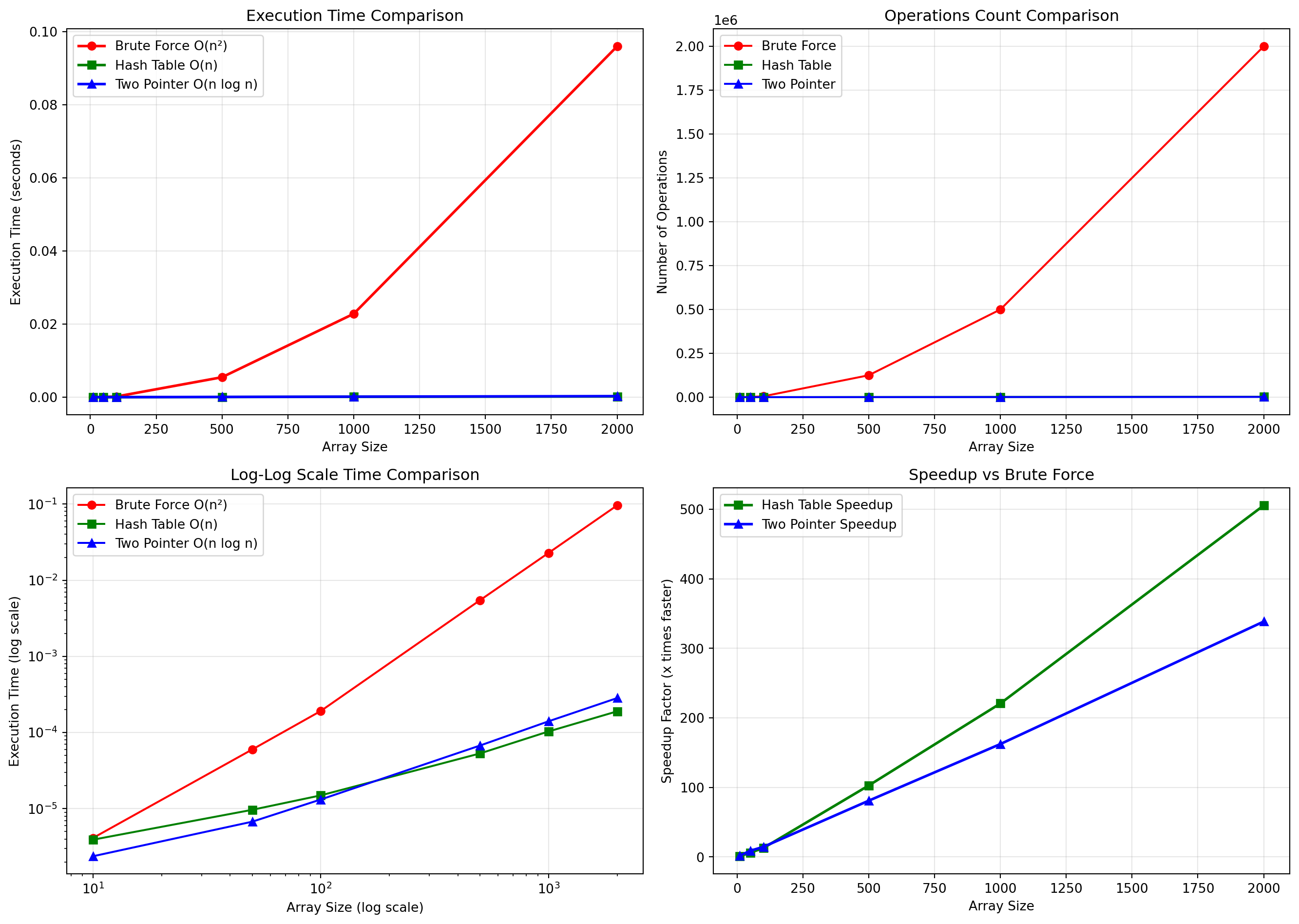
fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(14, 10))
# Execution time comparison
ax1.plot(sizes, results['brute_force']['times'], 'r-o', label='Brute Force O(n²)', linewidth=2)
ax1.plot(sizes, results['hash_table']['times'], 'g-s', label='Hash Table O(n)', linewidth=2)
ax1.plot(sizes, results['two_pointer']['times'], 'b-^', label='Two Pointer O(n log n)', linewidth=2)
ax1.set_xlabel('Array Size')
ax1.set_ylabel('Execution Time (seconds)')
ax1.set_title('Execution Time Comparison')
ax1.legend()
ax1.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# Operations count comparison
ax2.plot(sizes, results['brute_force']['operations'], 'r-o', label='Brute Force')
ax2.plot(sizes, results['hash_table']['operations'], 'g-s', label='Hash Table')
ax2.plot(sizes, results['two_pointer']['operations'], 'b-^', label='Two Pointer')
ax2.set_xlabel('Array Size')
ax2.set_ylabel('Number of Operations')
ax2.set_title('Operations Count Comparison')
ax2.legend()
ax2.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# Log scale comparison
ax3.loglog(sizes, results['brute_force']['times'], 'r-o', label='Brute Force O(n²)')
ax3.loglog(sizes, results['hash_table']['times'], 'g-s', label='Hash Table O(n)')
ax3.loglog(sizes, results['two_pointer']['times'], 'b-^', label='Two Pointer O(n log n)')
ax3.set_xlabel('Array Size (log scale)')
ax3.set_ylabel('Execution Time (log scale)')
ax3.set_title('Log-Log Scale Time Comparison')
ax3.legend()
ax3.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# Speedup factors
speedup_hash = [bf/ht if ht > 0 else float('inf')
for bf, ht in zip(results['brute_force']['times'],
results['hash_table']['times'])]
speedup_pointer = [bf/tp if tp > 0 else float('inf')
for bf, tp in zip(results['brute_force']['times'],
results['two_pointer']['times'])]
ax4.plot(sizes, speedup_hash, 'g-s', label='Hash Table Speedup', linewidth=2)
ax4.plot(sizes, speedup_pointer, 'b-^', label='Two Pointer Speedup', linewidth=2)
ax4.set_xlabel('Array Size')
ax4.set_ylabel('Speedup Factor (x times faster)')
ax4.set_title('Speedup vs Brute Force')
ax4.legend()
ax4.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Print speedup summary
print("\nSpeedup Summary (vs Brute Force):")
print("-" * 50)
print(f"{'Size':<10} {'Hash Table':<15} {'Two Pointer':<15}")
print("-" * 50)
for i, size in enumerate(sizes):
print(f"{size:<10} {speedup_hash[i]:<15.1f}x {speedup_pointer[i]:<15.1f}x")